10 min read
0
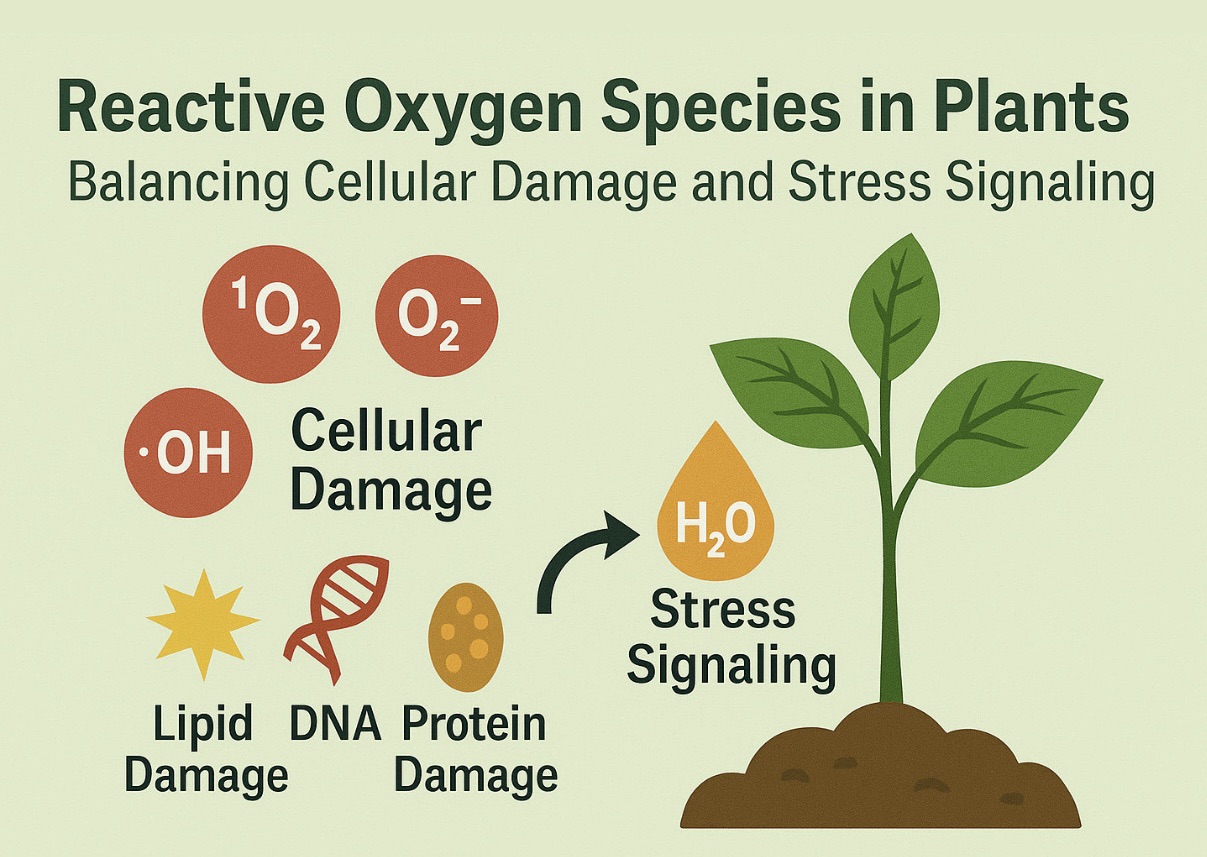
Reactive Oxygen Species in Plants: Balancing Cellular Damage and Stress Signalling
Plants live in a world of constant environmental uncertainty. Plants face various challenges such as the sweltering heat of a summer drought and the chilling grip of frost. Salinity creeping through irrigation water also poses a threat. Additionally, pathogens and…